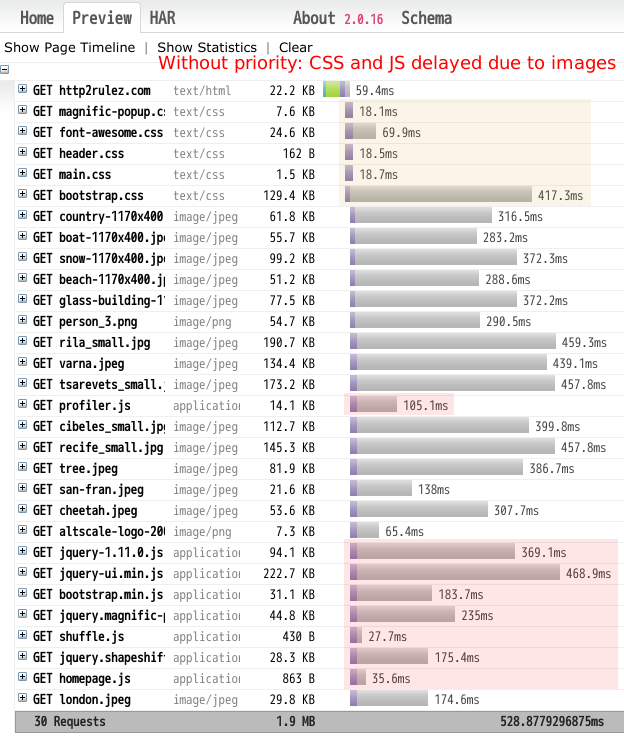
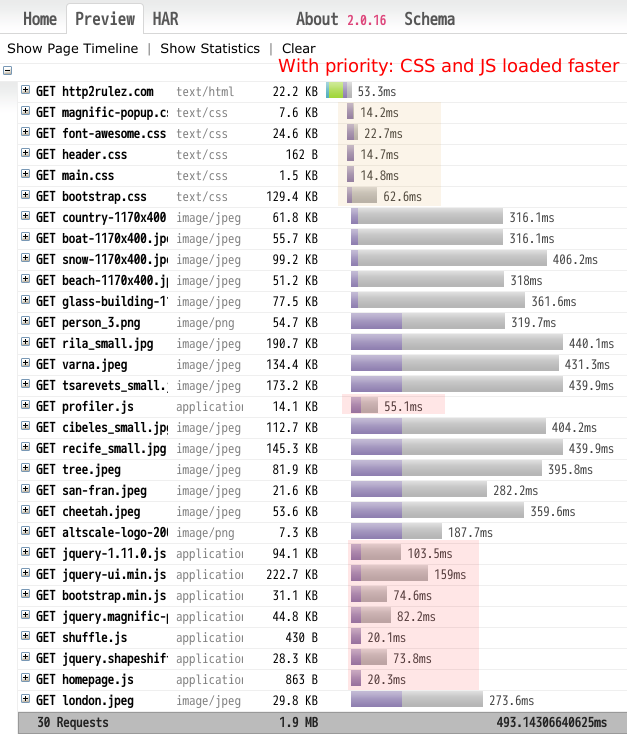
We released nghttp2 v0.7.6.
This release made several enhancements to the library. First we made
sending trailer part (trailer header field) easier. Previously,
nghttp2_submit_request() and nghttp2_submit_response() sets
END_STREAM flag set for the last DATA frame and we have no way to
send trailer part. To fix this issue, we added
NGHTTP2_DATA_FLAG_NO_END_STREAM flag. If application sets this flag
along side with NGHTTP2_DATA_FLAG_EOF in
nghttp2_data_source_read_callback, the library does not set
END_STREAM flag. Then the application can use new
nghttp2_submit_trailer() function to send trailer part, which is
a HEADERS frame with END_STREAM flag set. The all bundled
applications and libnghttp2_asio utilize this feature to send trailer
part.
Second enhancement is that now library refuses PUSH_PROMISE frame if
unacked local SETTINGS includes ENABLE_PUSH == 0 (disabling server
push). Previously the library refuses PUSH_PROMISE only after
SETTINGS are acked.
nghttpx has several enhancements in this release. It now accepts
multiple backend server addresses for HTTP/2 backend. Previously the
number of HTTP/2 backend server is limited to 1 per worker. In this
release, we added --backend-http2-connections-per-worker option to
specify the number of HTTP/2 backend connection per worker. As the
library gets enhanced support for trailer part, nghttpx now supports
trailer part for both HTTP/2 and HTTP/1. That means nghttpx can proxy
gRPC traffic, which requires trailer support.
we also fixed the bug that server push is broken after HTTP upgrade.
The another bug, which crashes nghttpx when upgrading HTTP/2 failed,
was also fixed.
Stefan Eissing wrote a patch to nghttpx to replace C++11
thread_local keyword with traditional pthread functions. Since Mac
OS X’s xcode toolchain does not support thread_local, it may be
possible to use nghttpx in multi-threaded mode on Mac OS X finally.
For nghttpd and nghttp, we added --trailer option to send trailer
part to exercise trailer part functionality.
For nghttp, Kazuho Oku kindly sent us a patch not to send pseudo-headers in HTTP Upgrade request (which itself is HTTP/1.1 message).
nghttp now treats request as success only if it sees the END_STREAM from peer. Previously it treated a request as success if it is closed (with/without error), before connection close.
We fixed nghttpd bug that “date” header field value is not updated.
For python binding, we fixed bug that push response header fields are not passed to callback in client library.
We rewrite libnghttp2_asio library and its API is not compatible to the earlier versions. Also we added client API. See libnghttp2_asio documentation about the example use of these APIs.